As en primeur 2018 picks up pace, we consider the 10 Bordeaux wines that any fine wine collector should acquire for their collection. These are based on the results of Wine Lister’s latest Founding Member survey, gathering the views of over 50 key players in the global fine wine trade.

You can download this slide here: 10 must have Bordeaux wines for your collection
The campaign in 2018 “won’t be a record breaker,” thinks Mathieu Chadronnier, MD of négociant CVBG, “but everything is there for it to work well.” There are also some potential pitfalls. In this article we consider the role that volume, pricing, and timing will play in the success of the 2018 en primeur campaign – already well underway.
Volume
In 2018, yields were often slightly below 2017 levels. Last year, frost damage provided a cover for releasing less volume into the market. Will mildew serve the same purpose in 2018? There were some extreme mildew casualties across the two banks, mainly for organic and biodynamic properties such as Palmer, which produced just 11 hl/ha. In Pomerol, L’Evangile made 20 hl/ha, less than half what it would have produced under conventional agriculture. In Pauillac, Pontet-Canet made just 10 hl/ha in 2018 – one third of its usual production, losing 15 hl/ha to mildew and another 5hl/ha due to dried out grapes.
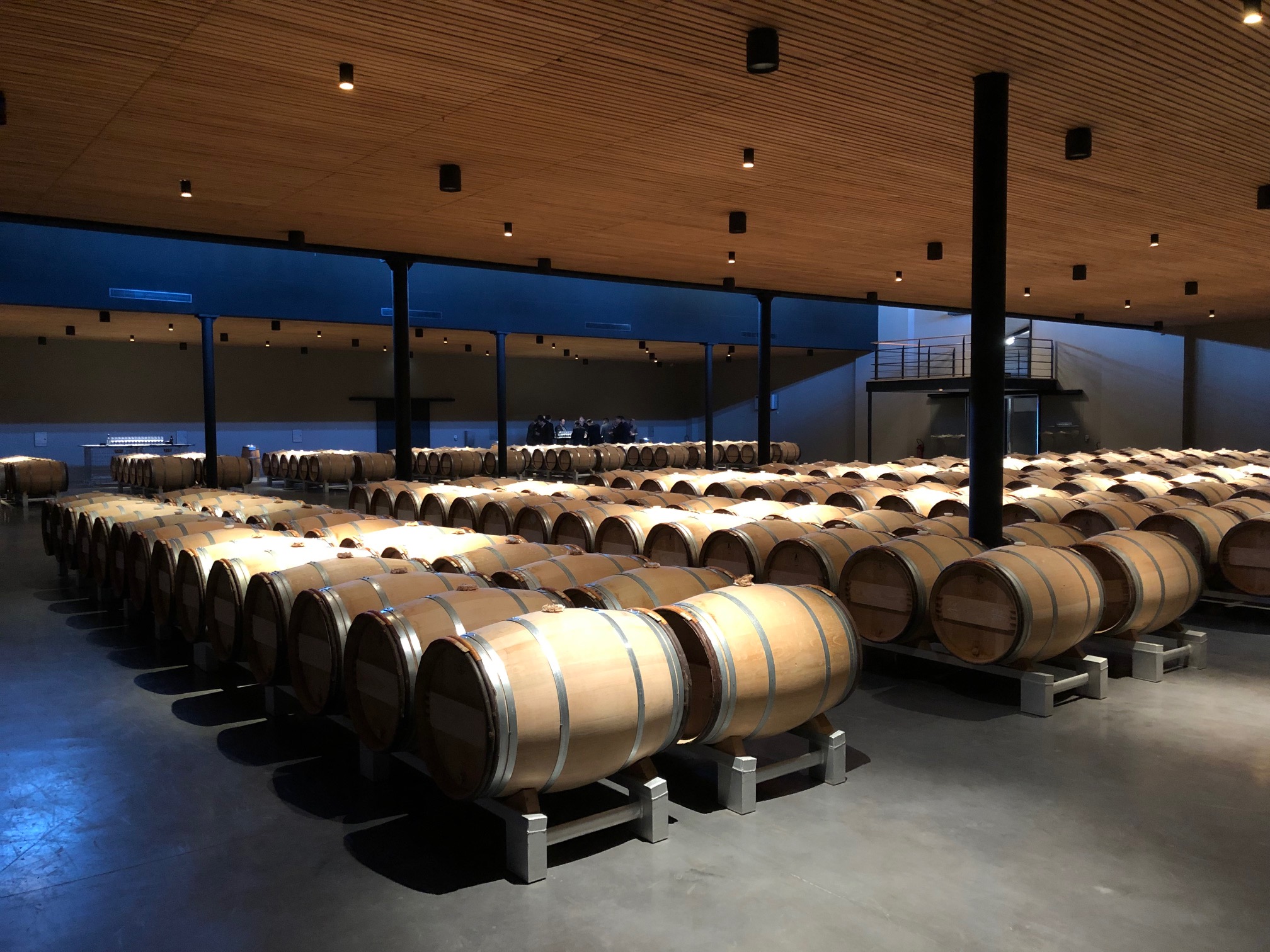 The cellar at biodynamic estate, Château Palmer, emptier than usual due to tiny production in 2018 following severe attacks of mildew.
The cellar at biodynamic estate, Château Palmer, emptier than usual due to tiny production in 2018 following severe attacks of mildew.
François-Xavier Borie, owner of Grand-Puy-Lacoste, believes that the real burning issue for en primeur is the volume released onto the market – or not. Some châteaux release nearly all their production, and others as little as 30%, keeping the rest back to create an artificial rarity in hope of selling the rest at a higher price later. Borie believes the right amount to release en primeur is “at least 80 percent,” cautioning that “releasing 30 percent and pretending it’s a real price is dangerous.”
Nicolas Ballarin of courtier Blanchy et de Lestapis agrees: “The problem of Bordeaux’s distribution is not in the price but in the fact that we don’t put enough wine into the market en primeur,” he states. “The real paradox is that knowing there’s none left at the château makes it more valued,” explains Ballarin, adding, “the négoce know they won’t get more.” He concludes that “prices only go up if there’s no more wine at the château.”
And after all, every producer’s objective is for their prices to go up. Many try to force this through their en primeur release price, while others let the market do the work. More than ever in 2018, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to bringing them onto the market.
As we saw in part I of our en primeur blog, 2018 was a vintage where producers’ decisions counted for a lot. In the words of Nicolas Glumineau, Managing Director of Pichon Comtesse, it is “a year with very important personal choices.” He was talking about the winemaking, but could just as easily be referring to the sale of the wine. “There won’t be any blanket tendencies,” says Frédéric Faye, Managing Director of Figeac, underlining that, “each château has to decide for itself and not look at its neighbours.”
Pricing
The only golden rule that the trade seem to agree on is that the 2018s should not be priced higher than the 2016s were upon release. “It would be a massive mistake for prices to be above those of 2016,” declared George Wilmoth, Head of Sales at UK merchant Justerini & Brooks. In Bordeaux, Edouard Moueix, Managing Director of Etablissements Jean-Pierre Moueix (producer and négociant), agrees, saying 2018 prices, “cannot be higher than 2016, it’s impossible.”
The exception to this rule of course, is where the 2016s have increased significantly since their release. Stephen Browett, Chairman of UK merchant Farr Vintners, reminds us that, “the vast majority of 2016 Bordeaux wines that customers bought en primeur are still available at delivery time at the same price as they paid two years ago, and in some cases less,” but there are exceptions, such as Lafleur, whose 2016 has increased 109% since release. When it released this morning, the château could therefore up its 2016 release price by 12% and still offer a 2018 that remains significantly cheaper than the current market price of the 2016.
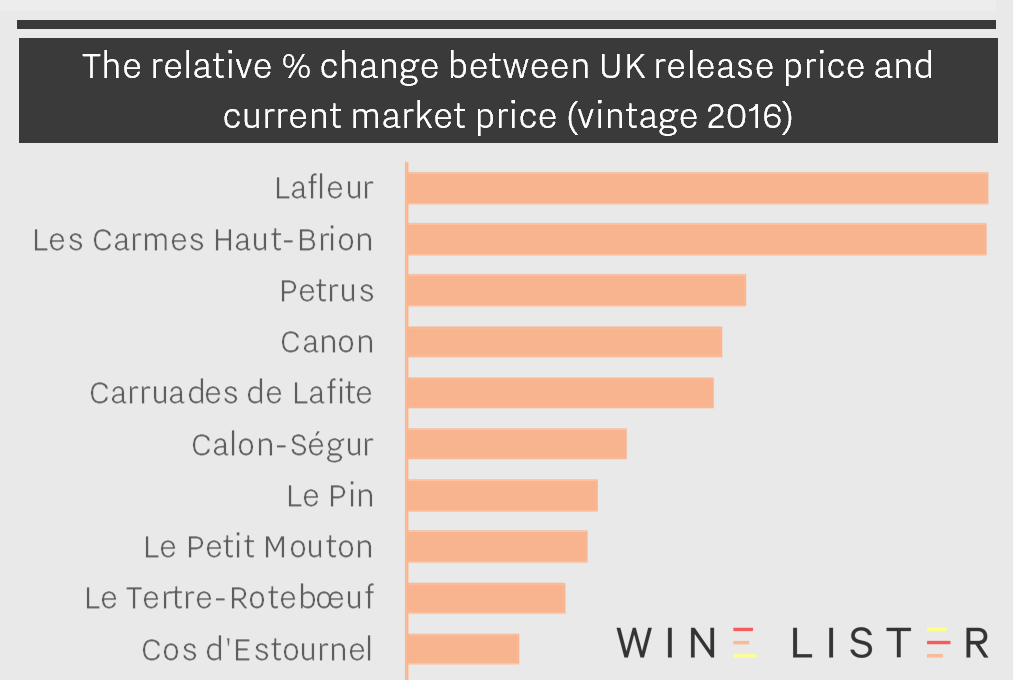 An excerpt from Wine Lister’s Bordeaux Study part I, showing the 10 2016 Bordeaux whose prices have increased the most since their release two years ago.
An excerpt from Wine Lister’s Bordeaux Study part I, showing the 10 2016 Bordeaux whose prices have increased the most since their release two years ago.
“At the end of the day the châteaux will charge what they can get,” states Mathieu Chadronnier, MD of négociant CVBG. The allocation system in Bordeaux means this is often more than what they should arguably be charging, because négociants don’t want to risk losing share to competitors in future years. However, some did refuse allocations in last year’s campaign, and this could happen again – and maybe on a larger scale – if prices are too ambitious.So far there have only been small instances of this.
Timing
The campaign is a precocious one, with Angélus releasing on 16th April, and a few dozen releases since, including well-known names Branaire-Ducru, Langoa-Barton, and Labégorce. However, it doesn’t really seem to have got going. Some of the Wine Lister team is just back from two days in Bordeaux speaking with négociants and courtiers on the Place, and there is a distinct lack of energy so far.
However, after yesterday’s bank holiday in France, and a handful of releases today, things are set to pick up pace in earnest next week. We expect a series of releases from châteaux that have historically judged their en primeur prices well, and this could breathe some life into the campaign. On the other hand, these are the very same châteaux who can actually conceive of increasing their prices, given their market value has risen sufficiently.
Some fear this will set the wrong precedent for their neighbours, which is why it is more important than ever for each property to consider its pricing strategy in the context of its own performance, and not what its neighbours are doing. Châteaux need to “make sure that their en primeur price to the consumer is lower than that of older vintages,” says Browett. In part I of our recent Bordeaux study, we looked at a case study of a hot property in Bordeaux that did just that in last year’s campaign.
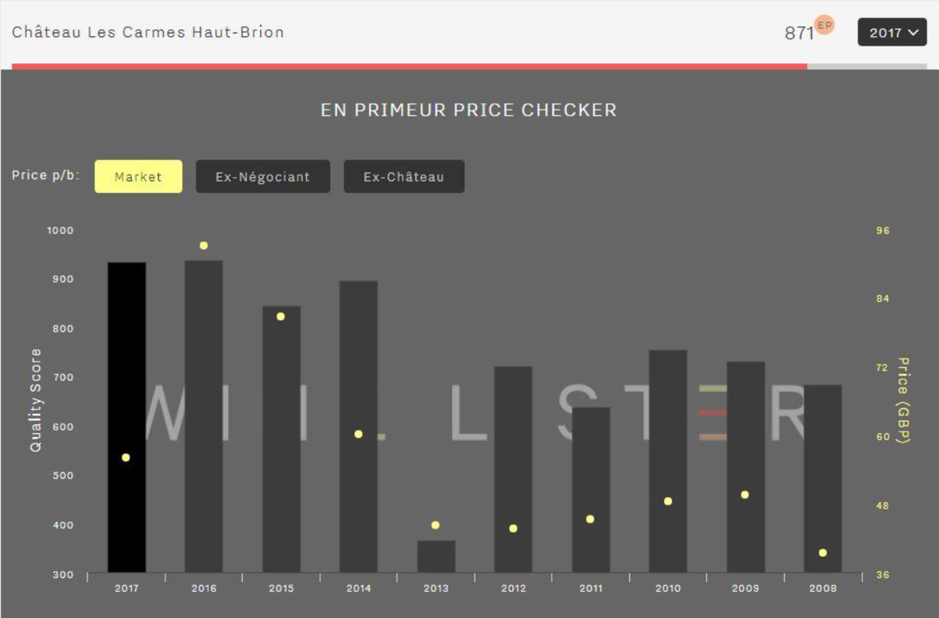 A masterclass in en primeur release pricing – the chart above shows Carmes Haut Brion’s 2017 release prices versus previous vintages on its day of release last year. Today the market price of 2017 is £65 (16% above release), and the 2016, £133 (109% above release).
A masterclass in en primeur release pricing – the chart above shows Carmes Haut Brion’s 2017 release prices versus previous vintages on its day of release last year. Today the market price of 2017 is £65 (16% above release), and the 2016, £133 (109% above release).
Let’s hope that more and more châteaux follow this formula as the campaign continues to unfold next week. The week after that is Vinexpo in Bordeaux, and most big-name releases will begin in earnest from 20th May.
Watch this space for the release of Wine Lister’s Bordeaux Study, Part II, before then.
Château Latour has released a parcel of their 2008 this morning. It is being offered in the UK at c.£425 per bottle. The factsheet below summarises its key points.
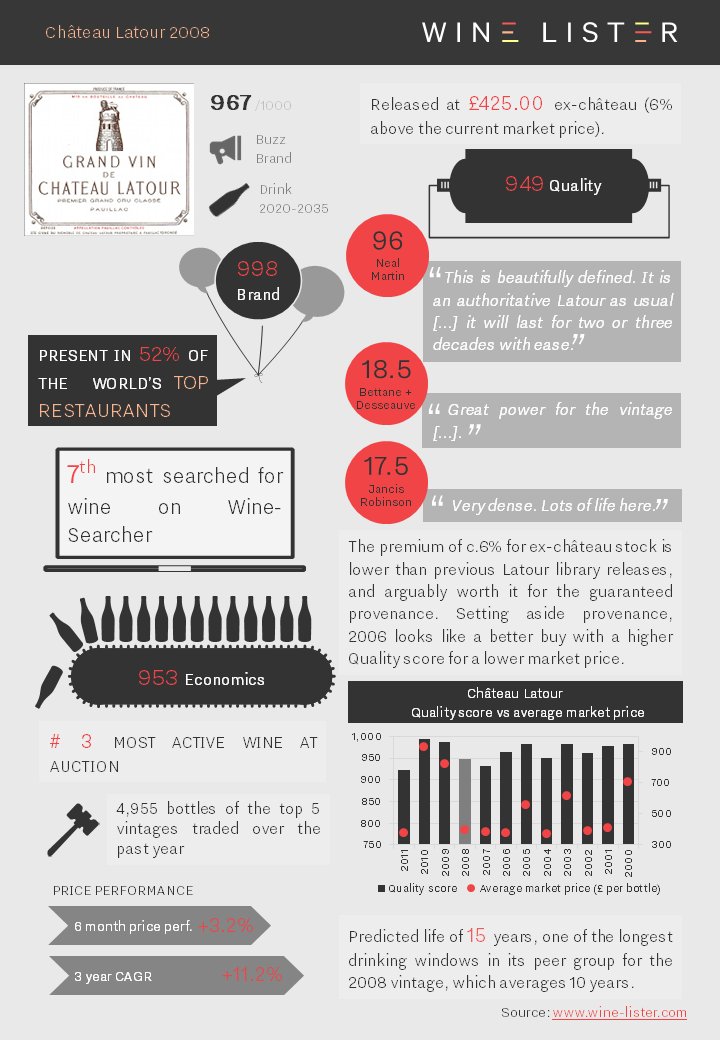
You can download this slide here: Château Latour 2008
Price and price performance have been hot topics for Wine Lister’s recent blog posts across several regions (Burgundy, Champagne, Tuscany). The Rhône Valley flies further under the radar than these as a region for investment, perhaps in part because its two distinct vineyard areas – North and South – are too different to be cast under the same umbrella. This week’s top five examines the highest prices in the Northern Rhône.
In first place is Domaine Jean-Louis Chave’s Hermitage Cuvée Cathelin. With an average price of £5,248 (per bottle in-bond), it is almost 20 times more expensive than the average of the other four wines in this week’s group. The small quantity of wine, made only in the best years, combined with a Quality score of 977 – the best of this week’s top five – go some way to explaining the four-figure price tag. (Interestingly, the most expensive wine in the Southern Rhône, Buzz Brand Château Rayas’ Chateauneuf-du-Pape, costs an average of £478, or just 9% of the Cuvée Cathelin).
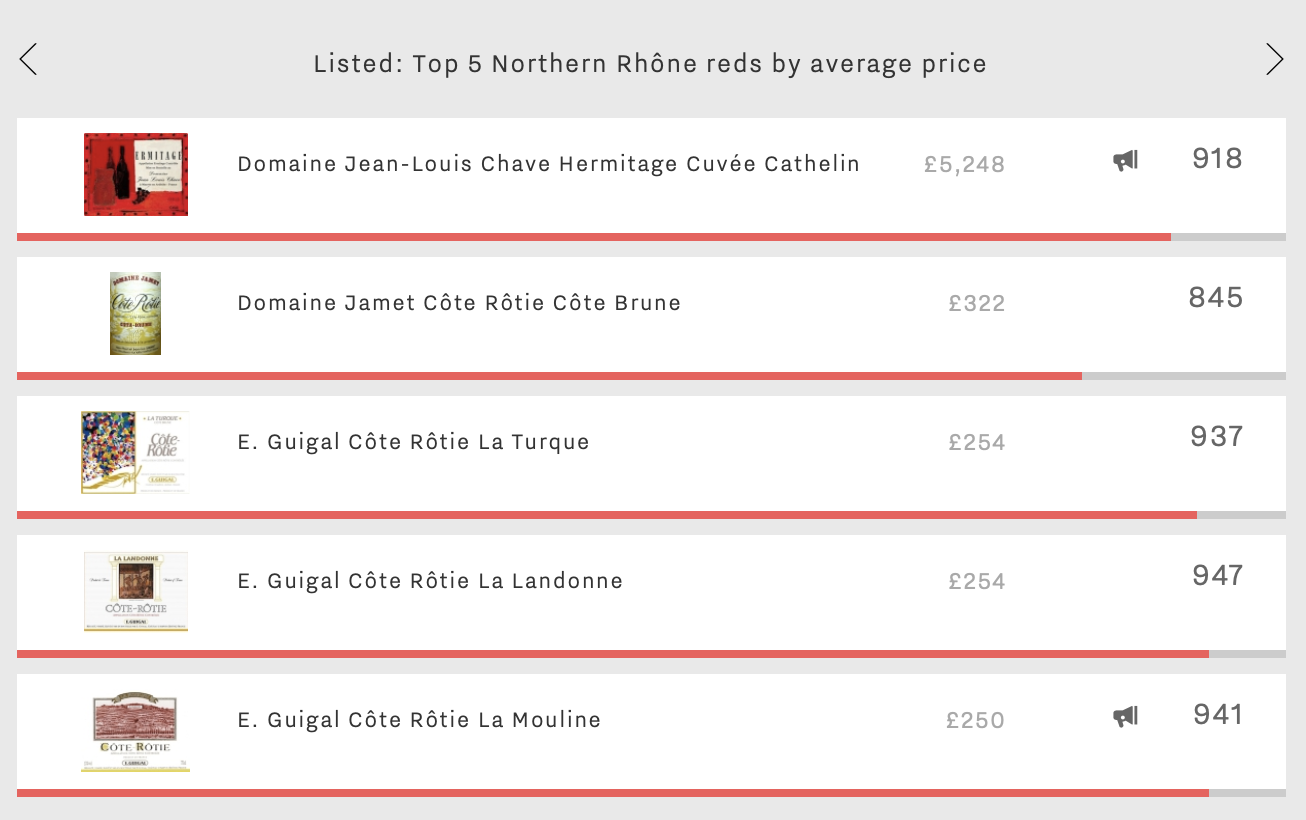
Back in the Northern Rhône, the next of this week’s top five is Domaine Jamet’s Côte Rôtie Côte Brune. Although £4,926 less expensive than this week’s number one, at £322 per bottle in-bond, it actually achieves the best three-year price performance, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.7%. With an average production volume of just 2,400 bottles per year, it is perhaps unsurprising that the wine’s Brand and Economics scores (at 763 and 759 respectively) are lower than its Quality score (946), as it appears in only 8% of the world’s best restaurants, and just three bottles were traded at auction internationally last year.
The remaining wines of this week’s top five hail from the same producer, Guigal, and come as a trio affectionately-known to the trade as “La-Las”. Though close together in price, it is interesting to see the subtle differences between these three Côte Rôtie across Wine Lister’s 13 score criteria.
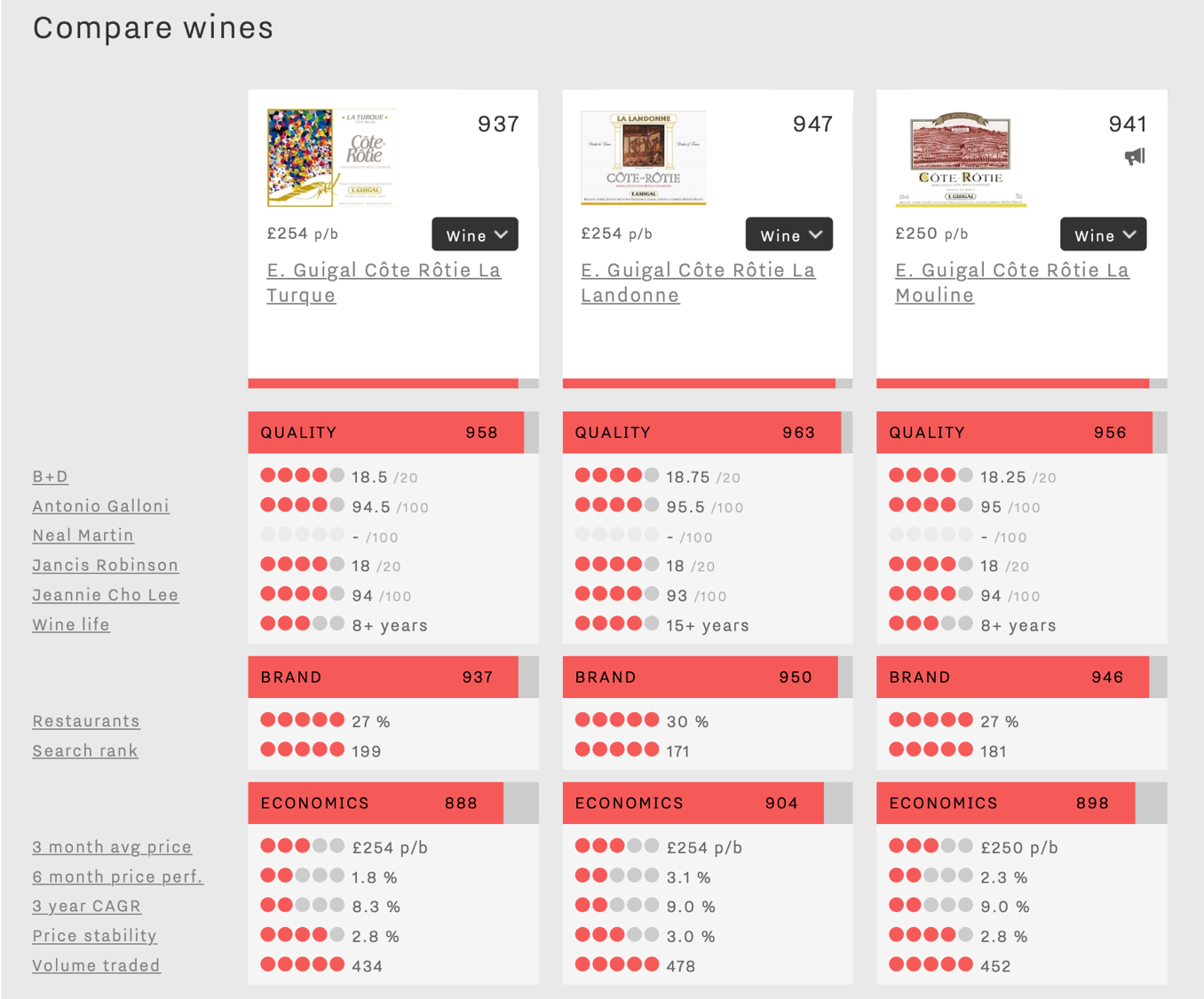
The chart above, created using Wine Lister’s Comparison tool, proves La Turque to be the lowest-scoring of the three overall. It shows slightly less demand with a lower search rank of 199 out of the c.4,000 wines on Wine Lister, whereas its siblings earn more monthly searches on Wine-Searcher. It also under-performs against the other two in economic terms, with lower long- and short-term price growth, and fewer bottles traded annually at auction.
By contrast, La Landonne achieves the top Quality score of 963 (and an average wine life just under twice that of its siblings), the best brand strength, and the highest average number of bottles traded annually at auction (478).
While La Mouline has the lowest average price of the three (£250 per bottle in-bond), it is the only one to earn Wine Lister’s Buzz Brand stamp, and achieves the joint-best three-year price performance with La Landonne – a CAGR of 9%.
With our founder, Ella Lister, just back from tasting the latest releases at Benvenuto Brunello in Montalcino, we thought we’d dig deeper into the data behind the appellation’s top wines. The pyramid system in the region means that most producers make at least three wines: in the middle, a Brunello di Montalcino DOCG Annata (or “vintage”); in good years, a Riserva (with longer ageing but also nearly always the best selection of grapes from the estate); and at the bottom of the pyramid, a Rosso di Montalcino DOC, producing fresher, approachable wines requiring less ageing.
This allows, and indeed encourages, a healthy level of selection in the region. At last weekend’s event, the vintages on show were 2013 Brunello Riserva (excellent), 2014 Brunello Annata (a tricky vintage, with some producers declassifying to Rosso di Montalcino), and Rosso di Montalcino 2017. There is also a trend in the Brunello DOCG towards vineyard-specific crus, such as Casanova di Neri’s Tenuta Nuova or Il Marroneto’s Madonna delle Grazie, both of which feature in this week’s top five: top Brunellos by Economics score.
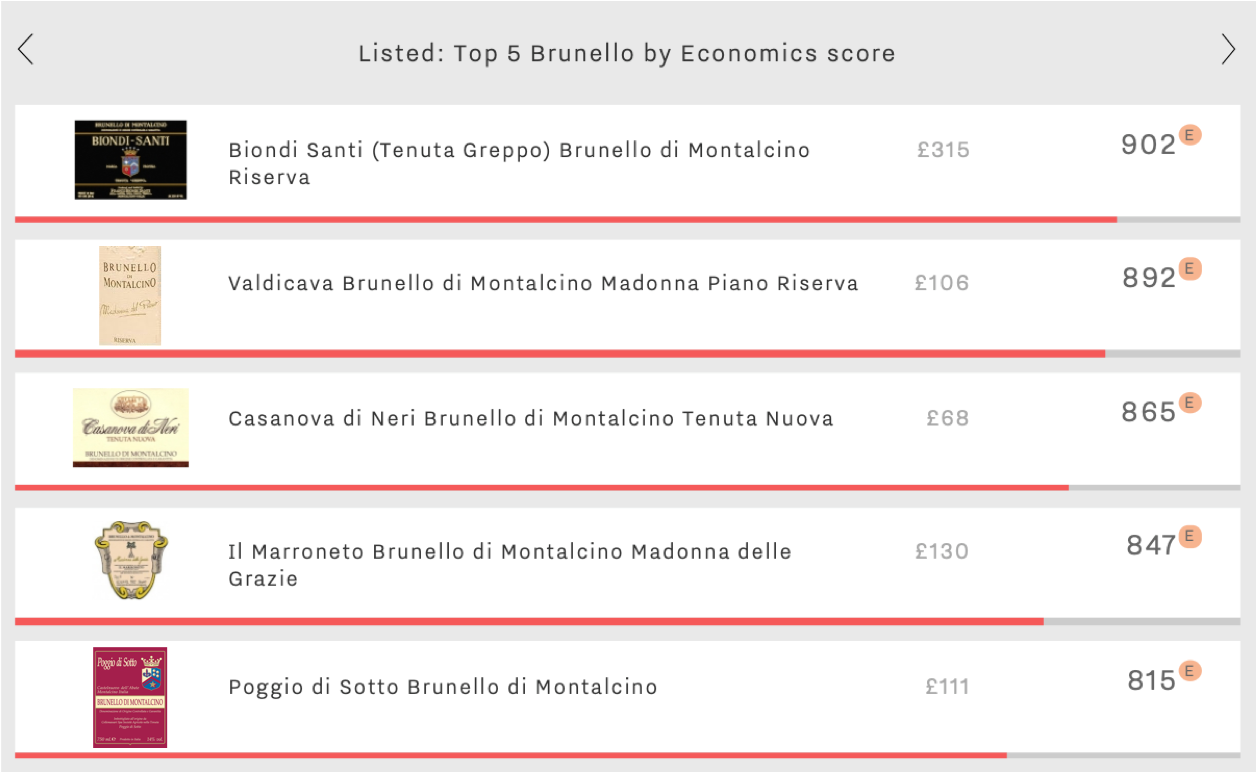
When examining the economic profile of Brunello wines, we see that Riservas tend to have higher Economics scores than Annatas, in line with their higher Quality scores. The best-performing Brunello by Economics score is Biondi Santi’s Brunello di Montalcino Riserva, with a score of 902. It earns the number one spot of this week’s top five with the highest price at £315 per bottle in-bond, and annual auction trading volumes of 458 bottles. The wine also outperforms the rest of the group for both Brand and Quality scores (904 and 938 respectively).
While Riservas are strong economically speaking, Annatas often have stronger Brand scores than their longer-aged counterparts, being produced in larger quantities and thus achieving greater visibility. In second place is Valdicava’s Brunello di Montalcino Madonna Piano Riserva, with an Economics score of 892, whereas its straight Brunello has a Brand score 57 points above its “big” brother, an example of the potential branding conundrum surrounding Brunello and other parts of Tuscany with a Riserva denomination. Nonetheless, the Riserva shows better price performance, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.2%, and an average of 257 bottles sold at auction annually.
Specific “crus” can also perform better than their straight Brunello Annatas in economic terms. In third place is Casanova di Neri’s Brunello di Montalcino Tenuta Nuova with an Economics score of 865. Despite having the lowest Quality score (841) and lowest price (£70) of the group, it earns this week’s second-highest Brand score (887).
In fourth place is Il Marroneto’s Brunello di Montalcino Madonna delle Grazie, the winery’s top cru, produced from grapes grown around the historic chestnut flour store house, and below the church by the same name. It has an Economics score of 847, benefitting from by far the best long-term price performance of this week’s top five, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.9%. Moreover, it sits just one point shy of this week’s number one in Quality terms (937) at 40% of the price – £130.
Rounding out the group is Poggio di Sotto’s Brunello, with an Economics score of 815.
While Super-Tuscans have been recognised for their investment potential for some time, Brunello still sits rather in the shadow of its Bordeaux-blend brothers. In Wine Lister’s first Tuscany market study, conducted in 2017, Brunello held nine places out of the top 25 Tuscan Economics scores. Today that number has increased to 14, as Brunello – Montalcino’s very own, highly ageworthy selection of the Sangiovese grape – goes from strength to strength.
At the end of last year, Wine Lister released its first ever Champagne report. As well as exploring a handful of key trends as identified by Wine Lister’s Founding Members, the report also sheds light on top Champagnes as compared to other regions in terms of economic performance.
Prices of the top Champagnes (Dom Pérignon, Krug Vintage, Louis Roederer Cristal, Salon Le Mesnil and Dom Pérignon Rosé) have seen a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% over the last six years. Relative to other major fine wine regions, this long-term growth is slow, as shown in the chart below, but also stable.
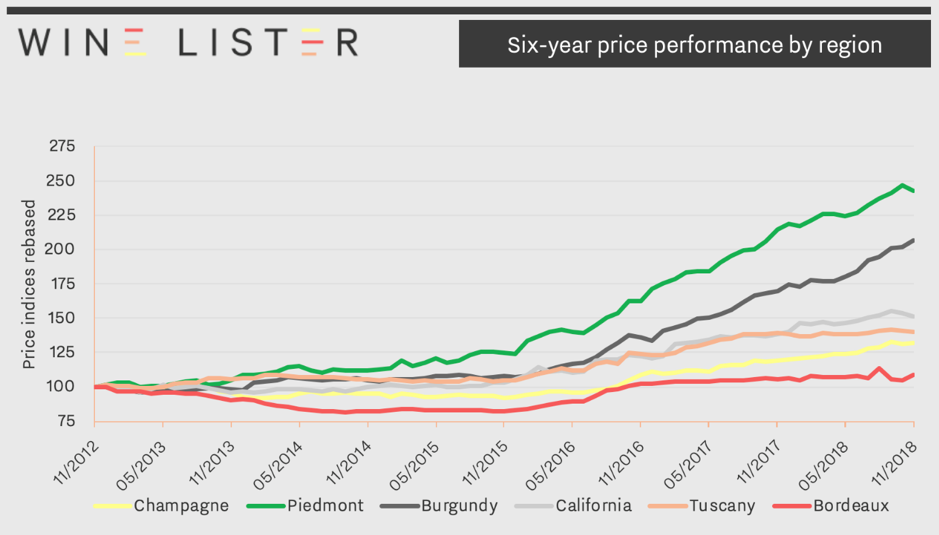
One notable advantage of Champagne as an investment option it its low volatility. Indeed, Champagne prices show a much better level of stability in the secondary market (deviating by just 2.5% from the average price over 12 months) than any other major fine wine region. Slow and steady wins the race.
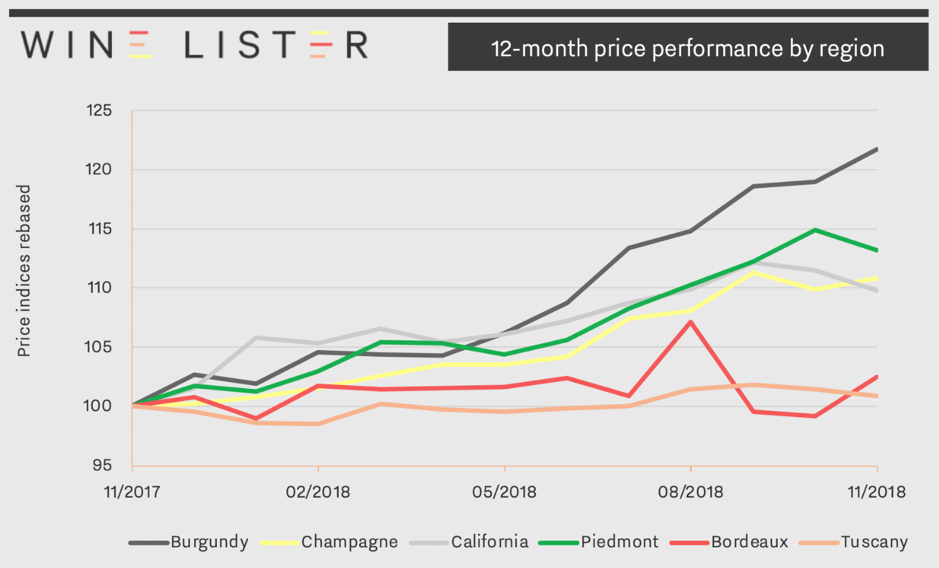
Moreover, recent price performance shows Champagne accelerating. Prices of top Champagnes are starting to grow at a faster rate than their counterparts in California, Bordeaux, and Tuscany, beaten only by Piedmont and the seemingly unmatchable Burgundy. Indeed, as of December 2018 top Champagnes had seen a 12-month price growth of 11%. The region’s potential for long-term investment is already being acknowledged by the trade, with one of our Founding Members, a top tier UK merchant commenting “Champagne (Salon especially) has experienced solid growth and has become a reliable investment for collectors”.
Salon Le Mesnil is the number one performing Champagne for price performance, with an Economics score of 978, closely followed by Krug’s Clos d’Ambonnay (962). Krug also tops the Champagne Economics charts with its Clos du Mesnil, Brut Vintage, and Collection. Interestingly the only NV Champagne to appear within the top 10 Champagnes for Economics is grower Jacques Selosse’s Brut Initial, with an Economics score of 911. Its price, £106 (per bottle in-bond), is a mere 18% of the average price of the other nine top Champagnes by Economics score.
To read more key findings from our in-depth Champagne study, read the free summary here. (The key findings and full study are also available to download in French on the Analysis page.)
Yesterday marked the annual BI Fine Wines’ 10 years on tasting, this year focusing on the iconic Bordeaux 2009s. Below we explore what light Wine Lister data has to shed on the 2009 vintage including quality, price performance, and best wines for good value.
Wine Lister’s holistic and dynamic approach allows us to not only see which appellations produced the vintage’s best wines, but also demonstrates if and how the market has since reacted to their relative quality.
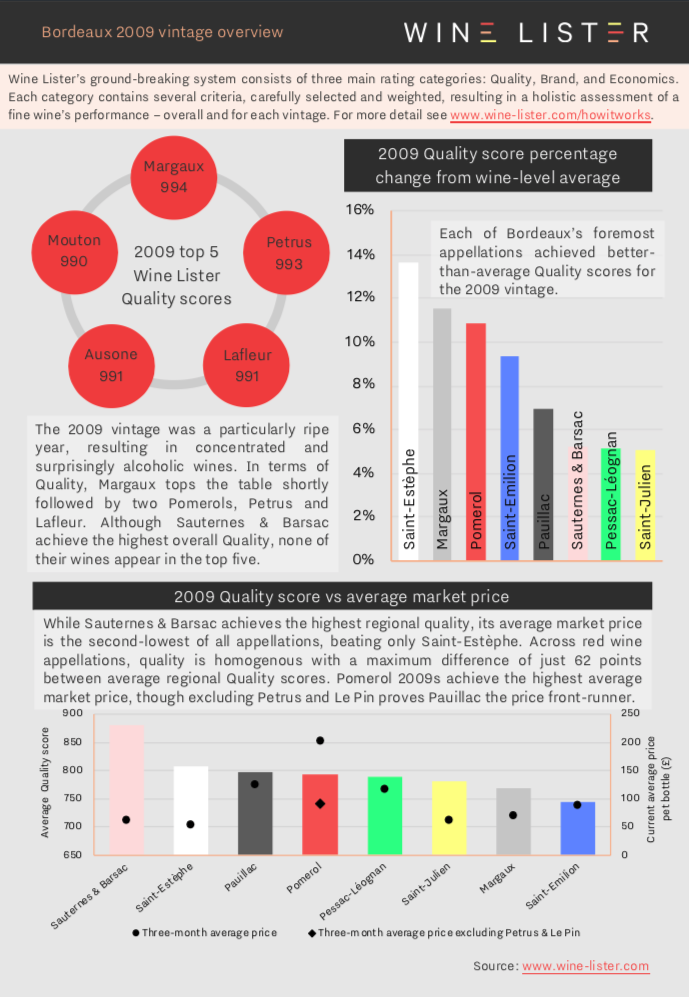
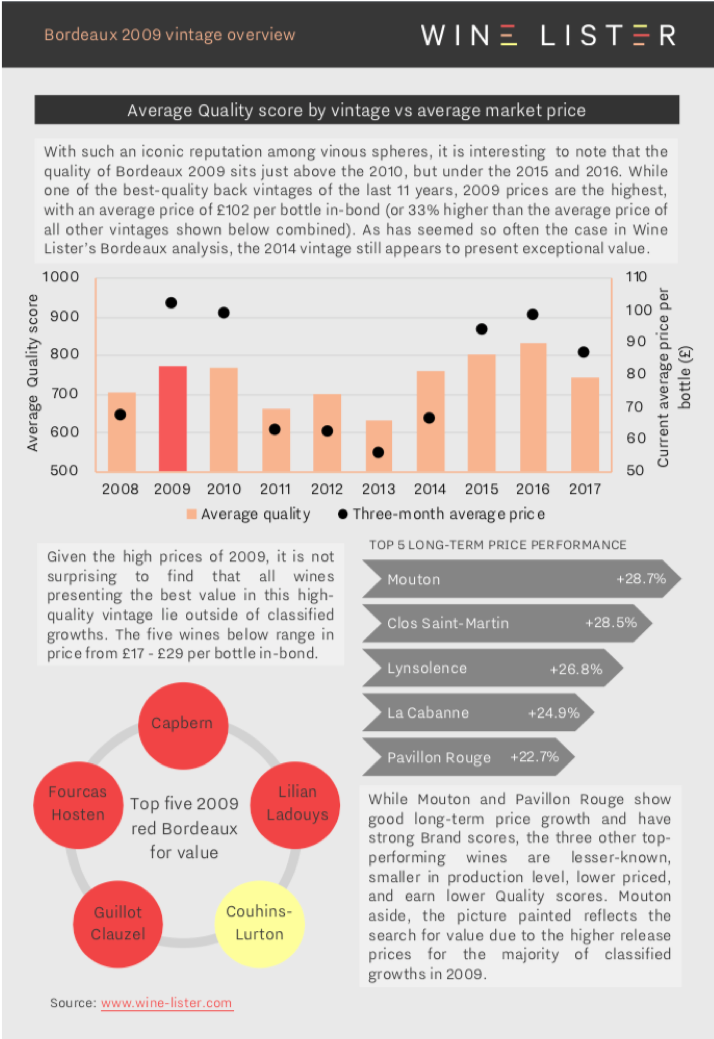
You can download the slides here: Wine Lister Bordeaux 2009 vintage overview
Featured wines: Margaux, Petrus, Lafleur, Ausone, Mouton, Capbern, Lilian Ladouys, Couhins-Lurton, Fourcas Hosten, Guillot Clauzel, Clos Saint-Martin, Lynsolence, La Cabanne, and Pavillon Rouge.
At the end of November Wine Lister spent three days in Burgundy meeting with producers across the length of the Côte d’Or. With more wine in their barrel cellars than for a very long time (in some cases more than ever), the mood was light and easy. The 2017 vintage saw the first normal-sized crop since 2009 (and 2018 was even more generous). “It’s the first year we’ve had barrels three rows high,” marvelled Thibaut Gagey as he showed me round Maison Louis Jadot’s vast cellars in Beaune, currently housing a record 6,000 fûts.

Thibaut Gagey in the Maison Louis Jadot cellars
The 2017 vintage is a “belle surprise” for Gagey, who admits, “we weren’t very confident at first.” This pleasant surprise was something expressed time and again by growers during our tastings of 2017 from barrel. With Burgundy Week about to unfold, here we look back over some of those conversations.
In Volnay, Guillaume d’Angerville calls the 2017 “a huge positive surprise.” He explained that “a lot of people had discounted the vintage early on,” because “they thought it would be diluted.” Our tastings, at Domaine d’Angerville and elsewhere, proved this supposition to be mistaken, the wines having taken on weight and complexity during their élevage. Jasper Morris MW refers to 2017 wines as “relatively homogenous, some with more concentration and others with less.” Either way, the wines are juicy, luminous, and downright delightful.

Tasting from barrel with Guillaume d’Angerville
Boris Champy, Manager at Domaine des Lambrays, calls the vintage both “classic” and “modern” at once, because he believes there’ll be many like it in the future. He compared 2017 to 2009. Angerville is reminded of the “tenderness” of 2007 (“but more substantial”) and the “harmony and elegance” of 2002 or 2010. “It’s going to give a lot of pleasure,” he pronounced. Gagey also cited 2007 for its positive surprise factor, and 2014 for its “accessibility”. The immediate pleasure these wines offer up is almost disconcerting, but this early approachability does not mean they won’t age. The 2017 might not be the longest-lived vintage, but it has everything in place for a good innings.
However, it “won’t be the vintage of the century,” Gagey states. “What it doesn’t have is that extra grip, depth, and drive of a great vintage,” confirms Morris. Meanwhile, the whites are superlative. “Apart from 2014,” Morris calls it the “most consistently good white vintage for a long time.”
The growing season was early, but otherwise unexceptional, apart, of course, from the threat of frost once more rearing its ugly head. This time, though, the Burgundians fought their nemesis with a thick veil of smoke. The fires they lit around their vineyards may have served to raise the temperature a fraction, but just as importantly, their smoke prevented the morning sun being magnified through the ice and burning the buds. And so, apart from in Chablis, yields were back to normal levels.
One might assume therefore that prices will come down – after all, the consistent increases over the last eight years have been put down to limited supply. This would be naïve, though, with global demand and secondary market values for Burgundy’s top wines continuing to spiral upwards, even to the bewilderment of some Burgundians (after the record-breaking results of the latest Hospices de Beaune auction of 2018 wines in November, Louis-Fabrice Latour, president of the BIVB (Bureau interprofessionnel des vins de Bourgogne), said he was “surprised prices went up, and by so much”).
The fact is, momentum is with Burgundy. The region’s top 50 wines grew in popularity by 26% over the last year, while Bordeaux’s search rank on Wine-Searcher remained stable, and other regions saw search levels drop. This means that top producers can almost certainly raise prices again this year and still sell through. We spoke to a few domaines who planned to do so, and some by significant margins. Mostly, though, prices should be flat on 2016 or see only modest increases (less than 10% up on 2016 prices). A minority have even come down in price. Either way, this is surely a vintage worth getting your hands on for unadulterated drinking pleasure.
Wine Lister’s Burgundy Market Study published this time last year for subscribers is now free for all to read. Download it in English or in French.
While Bordeaux may be best-known for its red blends, many a left-bank cru classé also produces a dry white, particularly in Pessac-Léognan. This week we examine the five most expensive dry white Bordeaux wines.
Whilst each of the five frequently stands in the shadow of their red counterpart (or flagship sweet white in the case of Y d’Yquem), their average price is in fact 28% higher (£260 vs £203). This is presumably due to the dry whites being produced in considerably smaller volumes than their red/sweet white counterpart (just 10% on average).
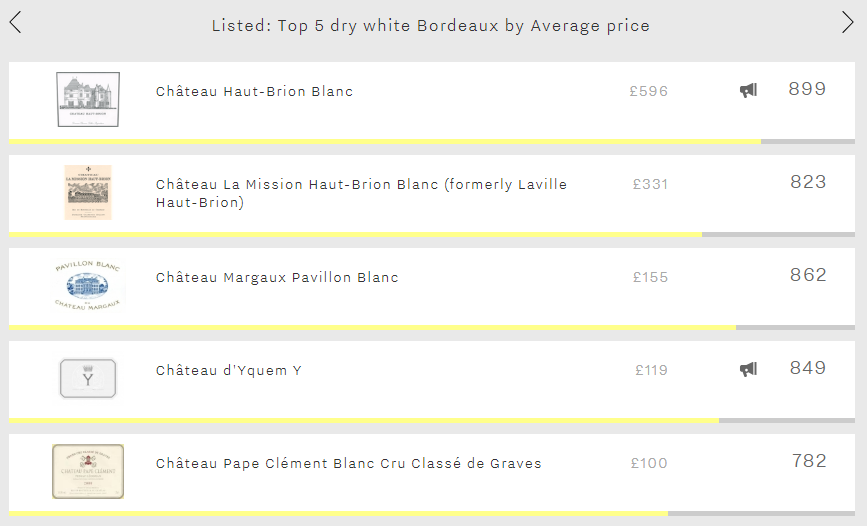
Leading the way is Haut-Brion Blanc at a cool £596 per bottle in-bond, 78% more expensive than Bordeaux’s second-most expensive dry white – its neighbour La Mission Haut-Brion Blanc – and well over three times the average price of the remaining wines in this week’s top five. Whilst its very low production, almost identical to La Mission Haut-Brion Blanc’s and thus the joint-lowest of the five, undoubtedly plays a part in its high price, the fact that it achieves the group’s best Quality and Economics scores (923 and 890 respectively) will also be a contributing factor. Aside from high ratings from each of Wine Lister’s partner critics, its excellent Quality score is also thanks to an average wine life of 10.3 years – the longest of all dry Bordeaux whites on Wine Lister. Indeed, the 2014 vintage, Haut Brion Blanc’s best ever with a Quality score of 975, “should drink well for years and perhaps even decades to come”, according to Antonio Galloni.
Next comes La Mission Haut-Brion Blanc at £331 per bottle in-bond. Relabelled in 2009, this was formerly Laville Haut-Brion. The 2011 is its best vintage since its relabelling, achieving an outstanding Quality score of 974, with Jancis Robinson – who tends to award it her highest scores of the group – calling it “one of the best Bordeaux 2011s”.
In third place is Margaux Pavillon Blanc (£155 per bottle in-bond). Whilst still priced considerably below the whites from Haut-Brion and La Mission Haut-Brion, it is closing the gap, courtesy of vastly stronger growth rates, with a three-year compound annual growth rate of 18% and having added 6% to its value since May. Over both the long and short-term, the two Pessac-Léognan whites have each grown at under half the rate of Pavillon Blanc.
Y d’Yquem is Bordeaux’s fourth most-expensive dry white, at an average price of £119 per bottle in-bond. Boosted by the immense clout of the château’s flagship sweet wine – which enjoys the joint-best Brand score of any wine on Wine Lister (999) – it has the strongest brand of this week’s top five (894). It does so thanks to featuring in the greatest number of the world’s best restaurants of the group (15%), just managing to nudge ahead of Haut-Brion Blanc (12%).
We return to Pessac-Léognan for Bordeaux’s fifth most-expensive dry white, Pape Clément Blanc (£100 per bottle in-bond). The 2017 was its best ever vintage, achieving an excellent Quality score of 903. Whilst it wasn’t quite able to match the scores of Haut-Brion and La Mission Haut-Brion (931 and 939 respectively), it represents considerably better value. At £100 per bottle, it is around one fifth the price of its Pessac-Léognan rivals.
Our latest Listed blog focused on the top Grand Cru Champagnes by Wine Lister score. As the holiday season approaches, we look at a different kind of ‘top five’ on a sparkling theme – five of the major trends for the Champagne region, determined by a recent survey of Wine Lister’s Founding members.
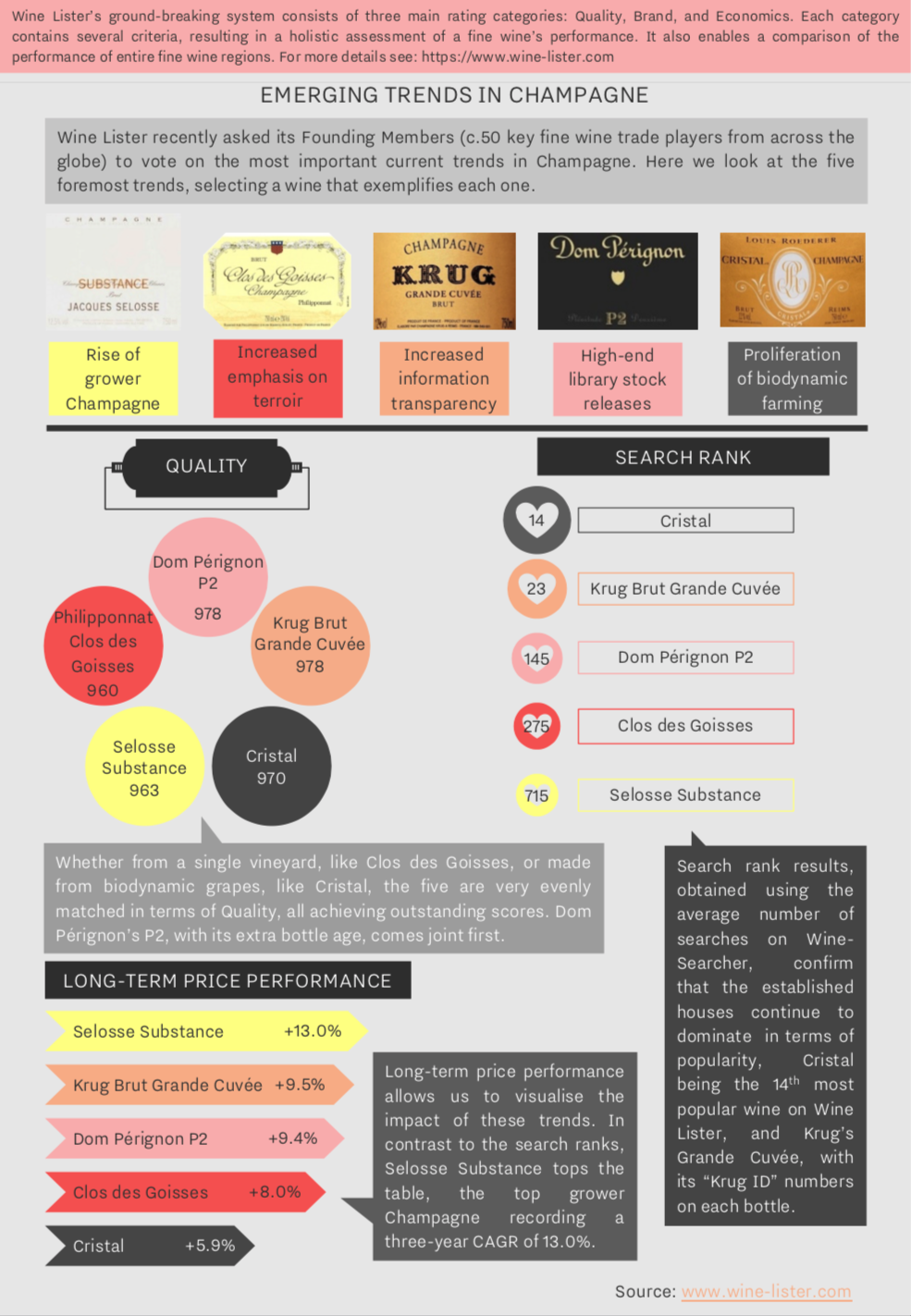
Key members of the global fine wine trade identified the rise of grower Champagnes as an emerging trend. Jacques Selosse reigns supreme, with its Blanc de Noirs La Côte Faron achieving the best Quality score of any grower Champagne on Wine Lister (975). Only an average of 1,250 bottles are produced of this each year – half of the production volume of its Substance Brut.
Founding Members also identified an increased emphasis on terroir as something to look out for. Single vineyard expressions of Champagne are well-known and already extremely sought-after, particularly Krug’s Clos du Mesnil and Clos d’Ambonnay. The latter achieves a Quality score of 970, just 10 points above Philipponnat’s Clos des Goisses, but is over 12 times the price (£1,867 vs. £147).
The phenomenon of increased information transparency is perhaps a sign that buyers are becoming more interested in Champagnes as wines, as opposed to just celebratory bubbles. Krug’s Grande Cuvée has used “Krug ID” numbers since 2011, allowing drinkers to see the vintages, vineyard plots, and grapes included in each bottle. Library releases also cater to more “wine-focused” buyers – Champagne Brand King Dom Perignon’s P2, or Bollinger R.D. are the obvious choices for this.
Finally, interest in biodynamically farmed Champagnes is on the rise, such as Louis Roederer’s Cristal, or any cuvée from Jacques Selosse.
Download a PDF of the slide above here.
First published in French in En Magnum.

 The cellar at biodynamic estate, Château Palmer, emptier than usual due to tiny production in 2018 following severe attacks of mildew.
The cellar at biodynamic estate, Château Palmer, emptier than usual due to tiny production in 2018 following severe attacks of mildew. An excerpt from Wine Lister’s Bordeaux Study part I, showing the 10 2016 Bordeaux whose prices have increased the most since their release two years ago.
An excerpt from Wine Lister’s Bordeaux Study part I, showing the 10 2016 Bordeaux whose prices have increased the most since their release two years ago. A masterclass in en primeur release pricing – the chart above shows Carmes Haut Brion’s 2017 release prices versus previous vintages on its day of release last year. Today the market price of 2017 is £65 (16% above release), and the 2016, £133 (109% above release).
A masterclass in en primeur release pricing – the chart above shows Carmes Haut Brion’s 2017 release prices versus previous vintages on its day of release last year. Today the market price of 2017 is £65 (16% above release), and the 2016, £133 (109% above release).










